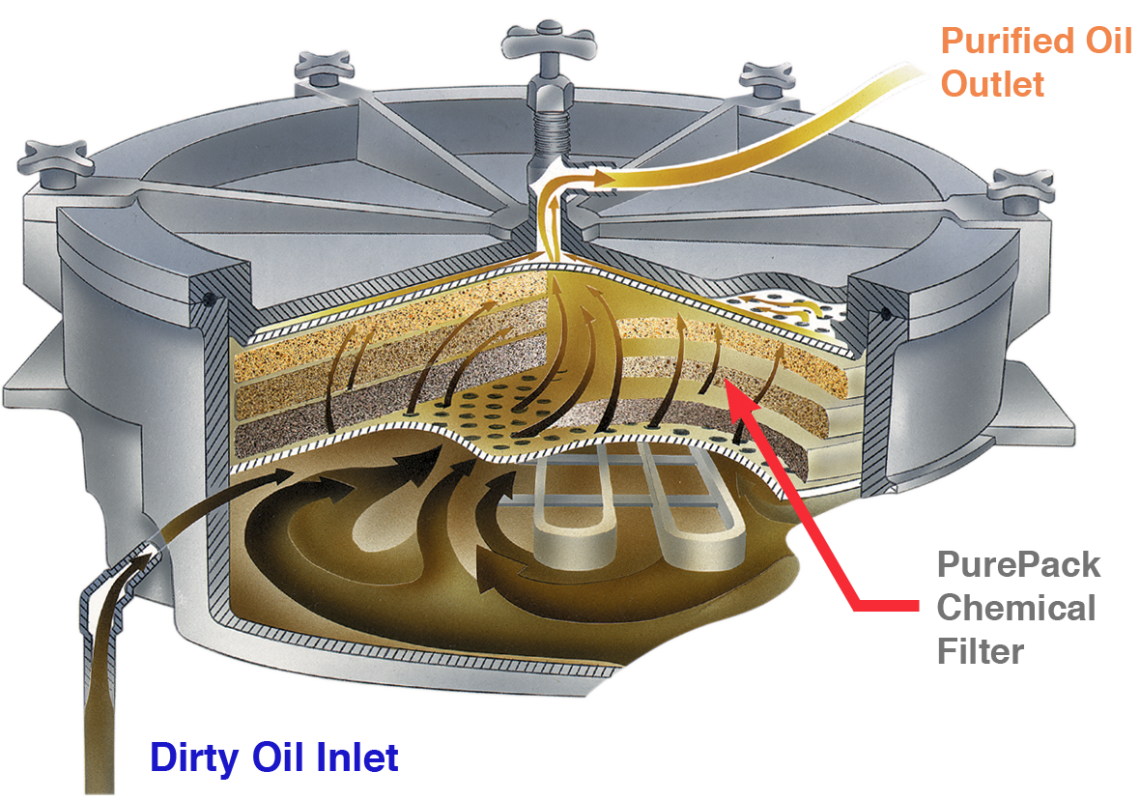
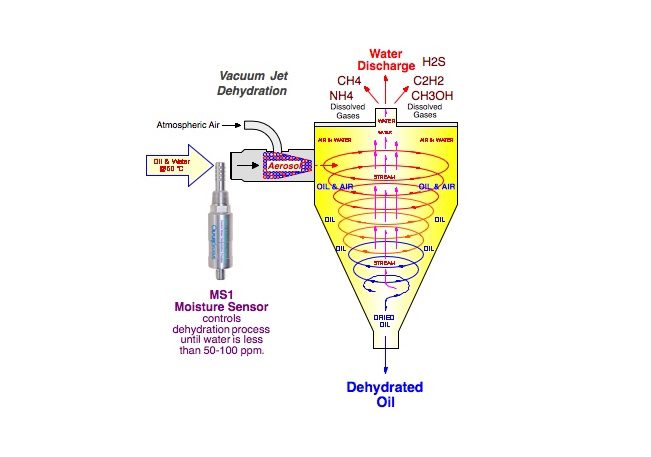
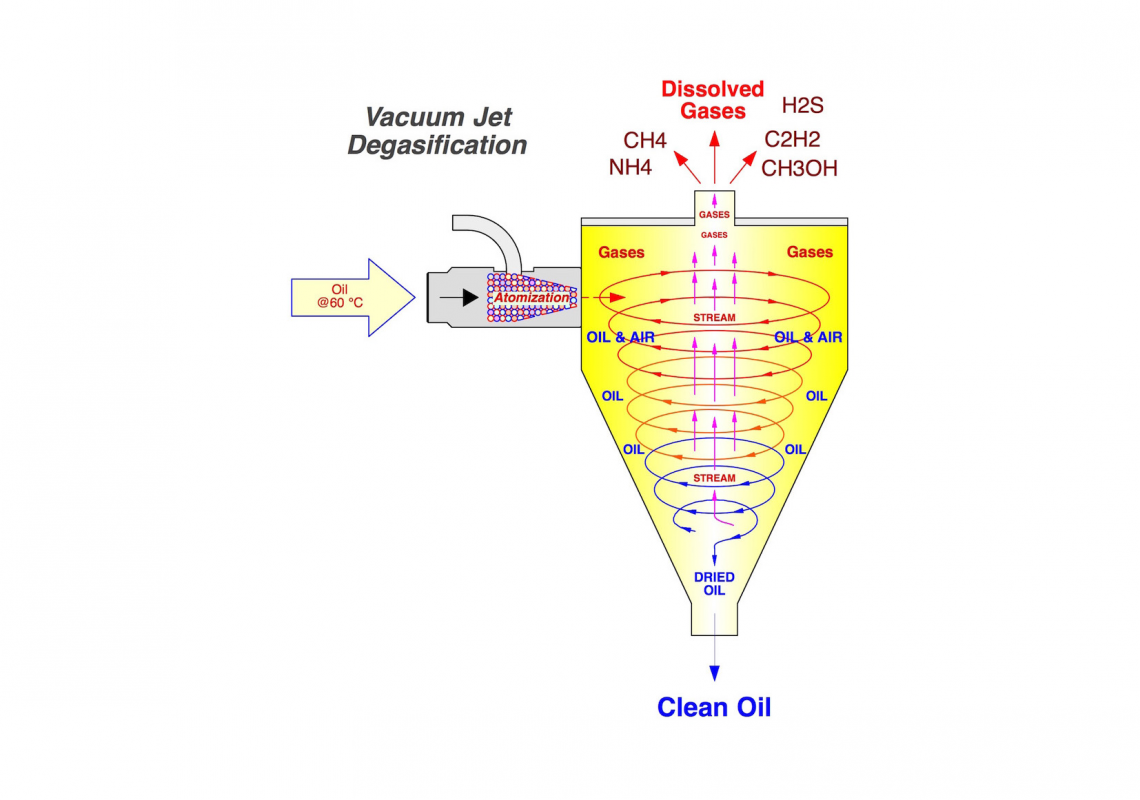
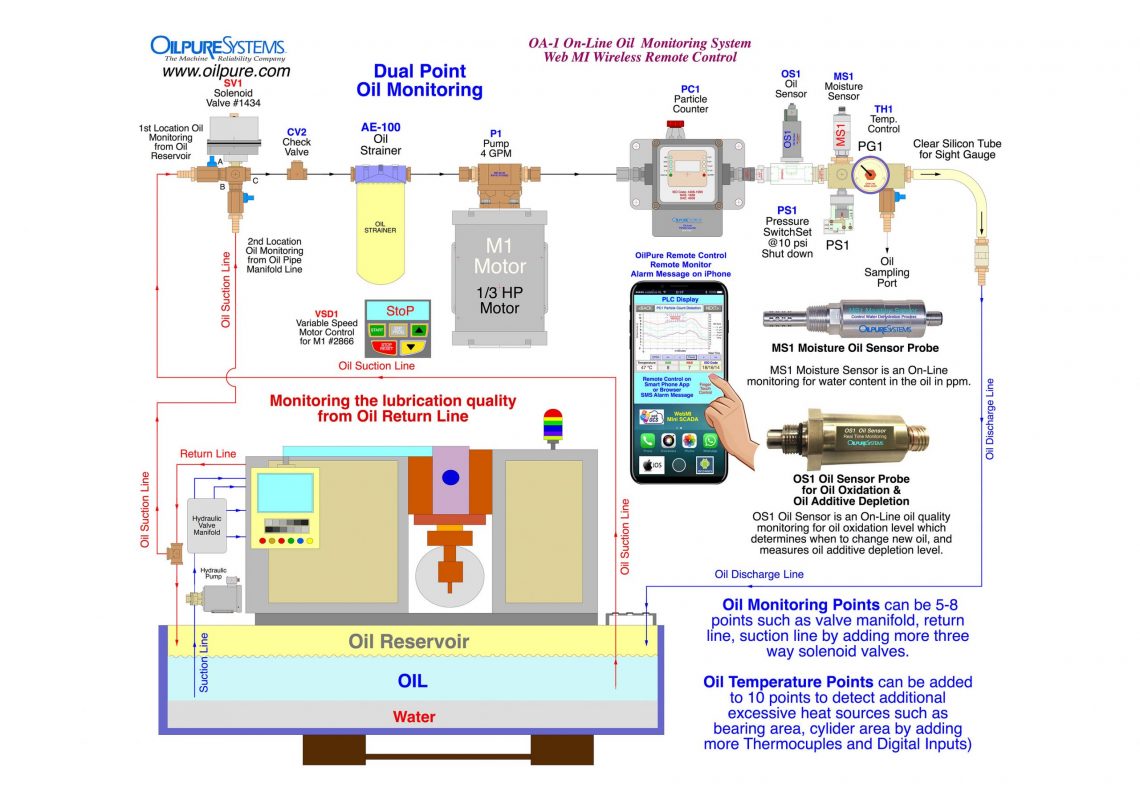
Oil Oxidation

- Oxidation-By-Products mostly comes from the depleted breakdown of oil additives. Actually they become bad additives after breaking down. ZDTP Zinc Dithiophosphate or Zinc additive is oxidized through heat and become Zinc Oxides or Varnish or Oxidation by Product in hydraulic oil.
- Varnish or Oil Oxidation By Product comes from various different forms and sources. Most of them come from the Breakdown of Oil Additives such as Zinc Oxides or Phosphorus Oxides which is similar to Salt or Oxides that came from TBN Additive. This derives from Carboxylic Acid of Hydrocarbon Base Oil and cluster into the Oxidation By-Products.
- Concurring Oil Oxidation or Auto Oxidation is a hidden Oil Oxidation by product that most user was not aware of how it happens in the oil as it does not came from Bad Oil Additives. This Concurring Oil Oxidation comes the built up of Electrostatic Charge from Oil Friction flowing through the Pleated paper Filter Media. This type of low micron paper filter is made of Polyester or Rayon Plastic Materials. The Oil Friction generates Electrostatic Charge and Electrify the Oil. Deprotonation Reaction with Hydrocarbon Base Oil generates Carboxylic Acid (R-COOH) and Carboxylate Anion that increases TAN Total Acid Number in the oil, thus promoting Internal Corrosion. This is one of the unsolved problem of Non Zinc lubricating oil that Varnish was found with no source of Zinc Oxides from oil additives.
- Anti Oxidant Additive helps control Free Radicals not to easily interact with Oxygen (Catalyst) from the air and Dissolved Oxygen in the oil to become Peroxides and Oxides. These Oxides or Varnish are typical Oxidation By Products in the oil.
- Peroxides and Oxides is Oxidation By Products in the oil will generate Polymers or Corrosive materials in the Oil:
- Polymers (Long chain hydrocarbon)
- Acids
- Aldehydes
- Alcohols
- Ketones
In general there are two type of Oil Oxidation:
- High Thermal Oxidation looks like hard brownish color, dried chocolate like sticking on part surface. They are very hard material but very Brittle.
- Low Thermal Oil Oxidation looks like Greasy soft material stick on part surface.





Hydrocarbon Oxidation Mechanism:
- Initiation
- R-H + O2 (Oxygen) —–> R° + HOO (Water) ……… with Heat
- ROOH (Peroxide) —–> RO° + OH° (Hydroxyl)
- Propagation R° + O2 —–> RO2°
- RO° + O2 —–> RO2°
- RO2 + RH —–> RO2H + R°
- HO° + RH —–> R° + H2O
- Termination
- 2RO2° —–> Non Radical Products
- R° + ROO° —–> ROOR (Peroxide)
- R + R° —–> R-R
- Summary of Oxidation Control
- RO2° = Additive Molecular Chain Breaking
- Hindered Phenolic
- Aromatic Amines
- ZDTP
- Copper Salts
- RO2H (Peroxide) = Peroxide Decomposition
- ZDTP
- Sulfur Components (Base Oil)
- RO2° = Additive Molecular Chain Breaking
- Oil Additives can be prescribed and refortify to the used clean lubricants. However, this used lubricants must be clean and free of Solid Particle, Water and Oil Acidity or Oxidation. This process is called “Supplement Additive Refortification (SAR)” to enhance oil quality on existing used lubricants.
- If used lubricant is not clean. adding oil additives will cause the Backfire creating more rapid Oil Oxidation. The adding additives will turn into bad additives very soon.
Oil Oxidation Caused by Low Micron Oil Filter from the On-Line or Full Flow Filter and Returned Line Filter
Hidden Oil Oxidation occurs slowly from Low Micron Oil Filter that are mostly uses in the industries. This type of oil oxidation is so called “Concurring Oil Oxidation” causing the short oil life. The Anti Oxidant Additive is constantly working to retard the oil oxidation reaction and slowly depleted at a higher rate. After the Anti Oxidant Additive become inadequate to balance the oil oxidation reaction, there will be more oil deterioration coming after the additive depletion rate is below normal. This is how lubricant become deteriorated faster than its normal life.
It is easier to notice that the Non Zinc Additive in Hydraulic Oil shows most of the Concurring Oil Oxidation where there is no Zinc in the system and no Zinc Oxides which is a component of Oxidation by product. The source of Oil Oxidation by Products came from Low Micron Oil Filter.

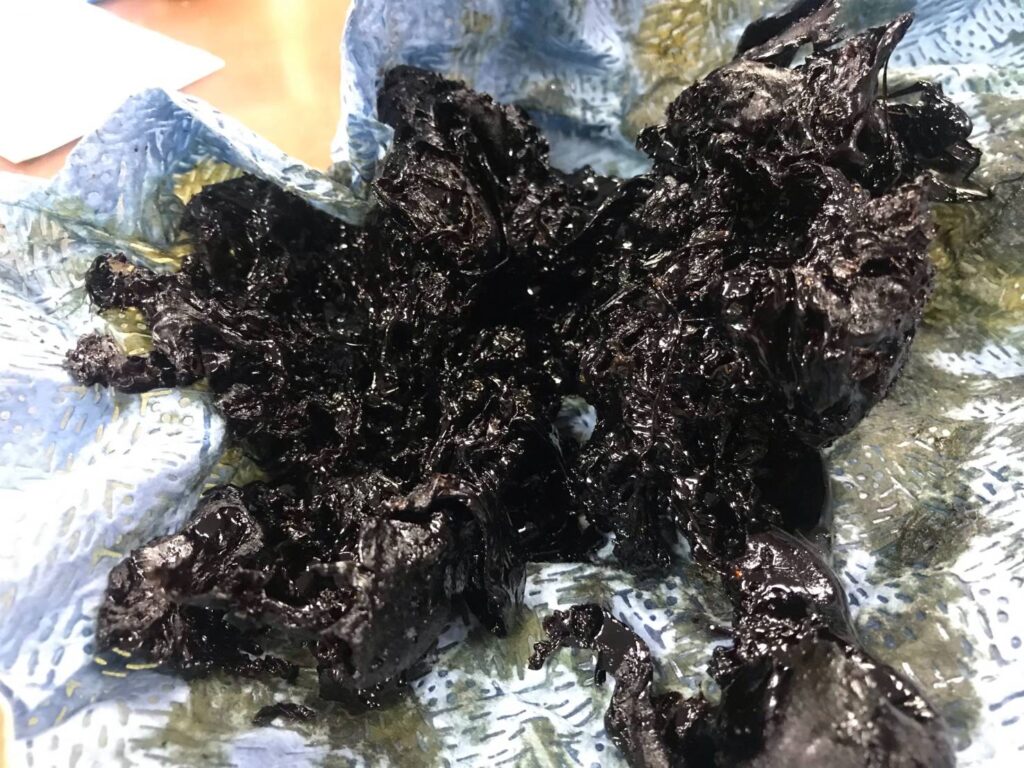
Pleated Paper Filter material that is made of Cellulose, can only have the smallest retention of 10 micron Nominal Value. However, the 10 micron Nominal Value is still to large to hold typical hydraulic component Tolerance. So the filter manufacturer has to use other materials, beside cellulose that has much lower retention in the filter media. They use Filter Materials such as Rayon, Polyester, Nylon that has fibrous structure having filtration retention of 1-6 micron Absolute Value.
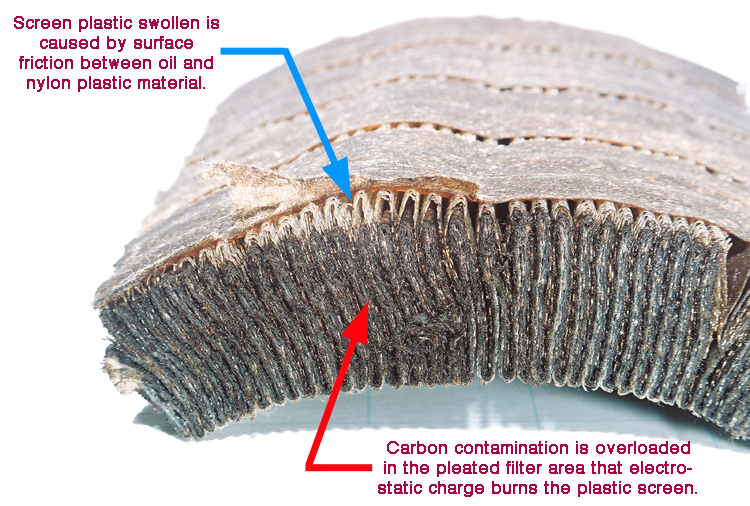


This plastic fibrous materials is the real source of Concurring Oil Oxidation that generates Electrostatic Charge to the oil from oil friction while the oil is flowing through fibrous filter media. The oil is electrified and expanding its its + – Ion through out lubrication in the system affect the internal component corrosion.
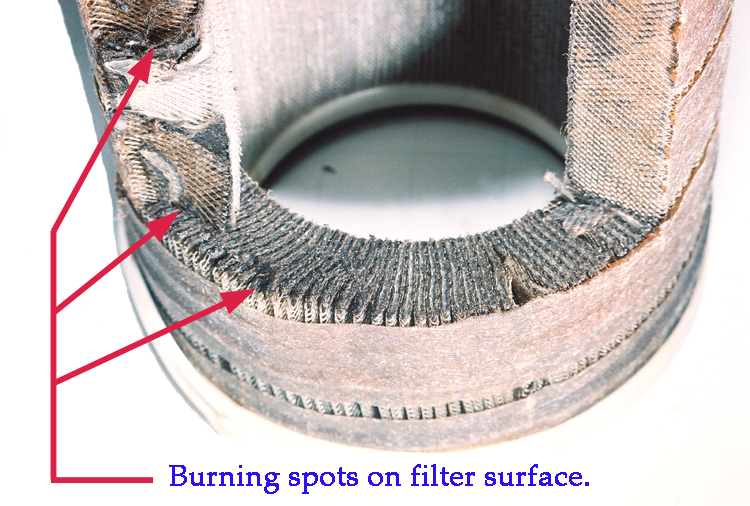
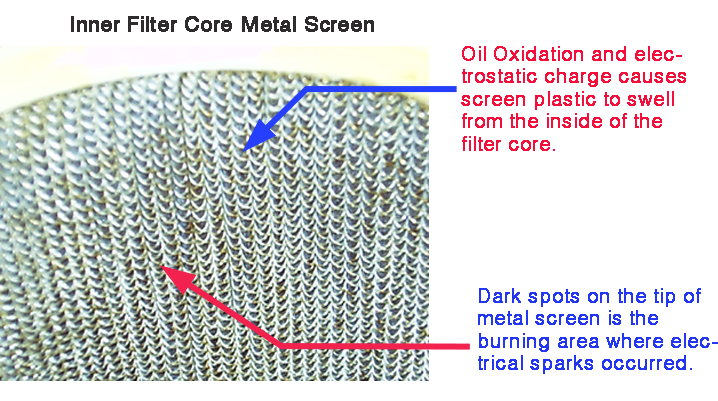
The exchange of + – Ion charge causes chemical changes in the oil and Spark from the Electrostatic Charge stimulates the Concurring Oxidation or Auto Oxidation. There are more exchange of Free Radicals and Charge Ions especially in the Low Viscosity, Low Conductivity and Low Water Content in the oil. This is normally found in transformer oil.
Concurring Oil Oxidation occurs in the the oil all the time when there is enough Oil Flow Rate and Friction on Filter Surface. User would have no idea how this oil deterioration could happen in the oil. User selects Oil Filter based on the particle count oil cleanliness in ISO Code or NAS Class. The Low Micron Rating Filter is chosen for the highest cleanliness but it also generate more Oil Friction. Most users are ignorance about this problems and have no idea how this happens.
- This oil oxidation can be noticed by reviewing on the hydraulic components as follows:
- Oil Reservoir Sigh Gauge starts to distort the color from clear plastic into a brownish color and it can not be clean by wiping out with towel.
- Oil Reservoir Tank Wall usually shows the brownish stain on the side wall and can not clean by wiping out with towel.
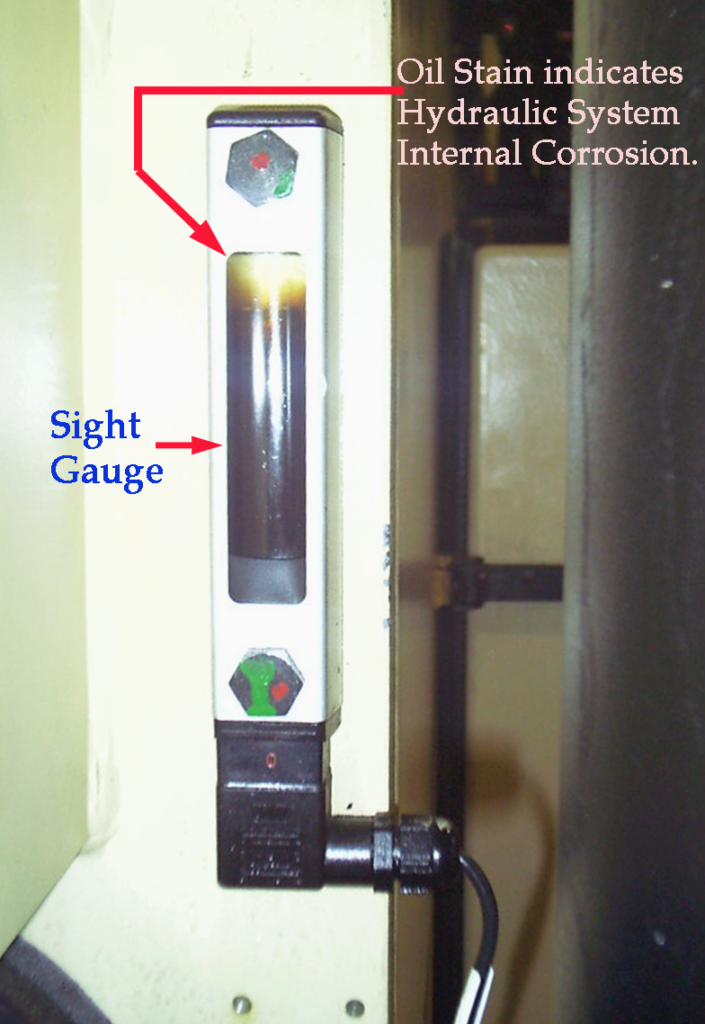


Oil Oxidation Caused by Hydroxyl (OH–) from Previous Water Breakdown in the Lubricating System
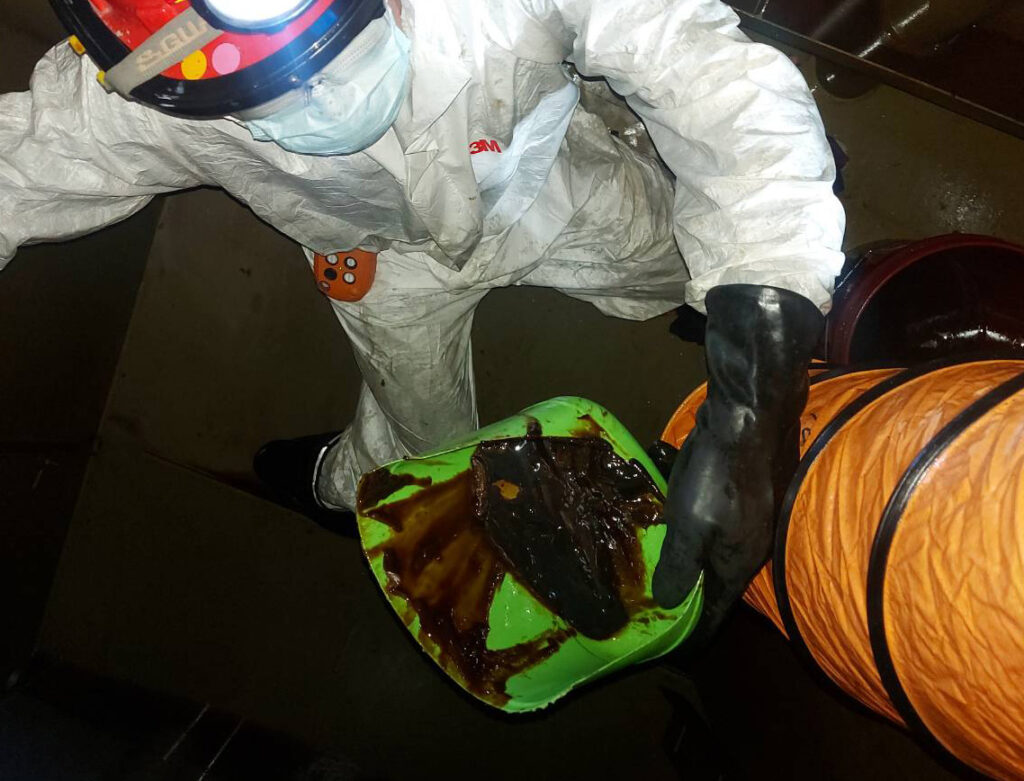
Oil Oxidation can occur from Hydroxyl (OH–) causing from previous water breakdown into the lubricating system. You can look at the Oxidation Paste that stick inside bottom of the oil reservoir as looks like the below photo. This describes the oil oxidation that came from the previous water breakdown.

The above oil oxidation by product photo came from Husky Injection molder having water breakdown several time in the US manufacturing plant.


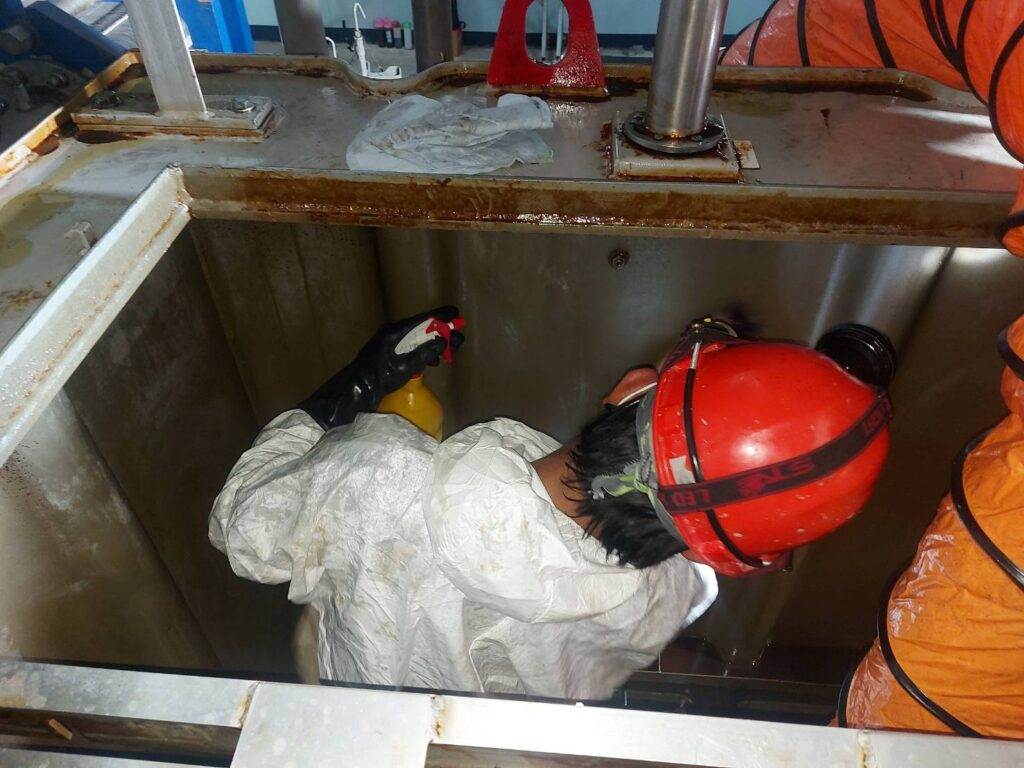
These oil oxidation by product photos came from Paper Mill plant in Thailand.
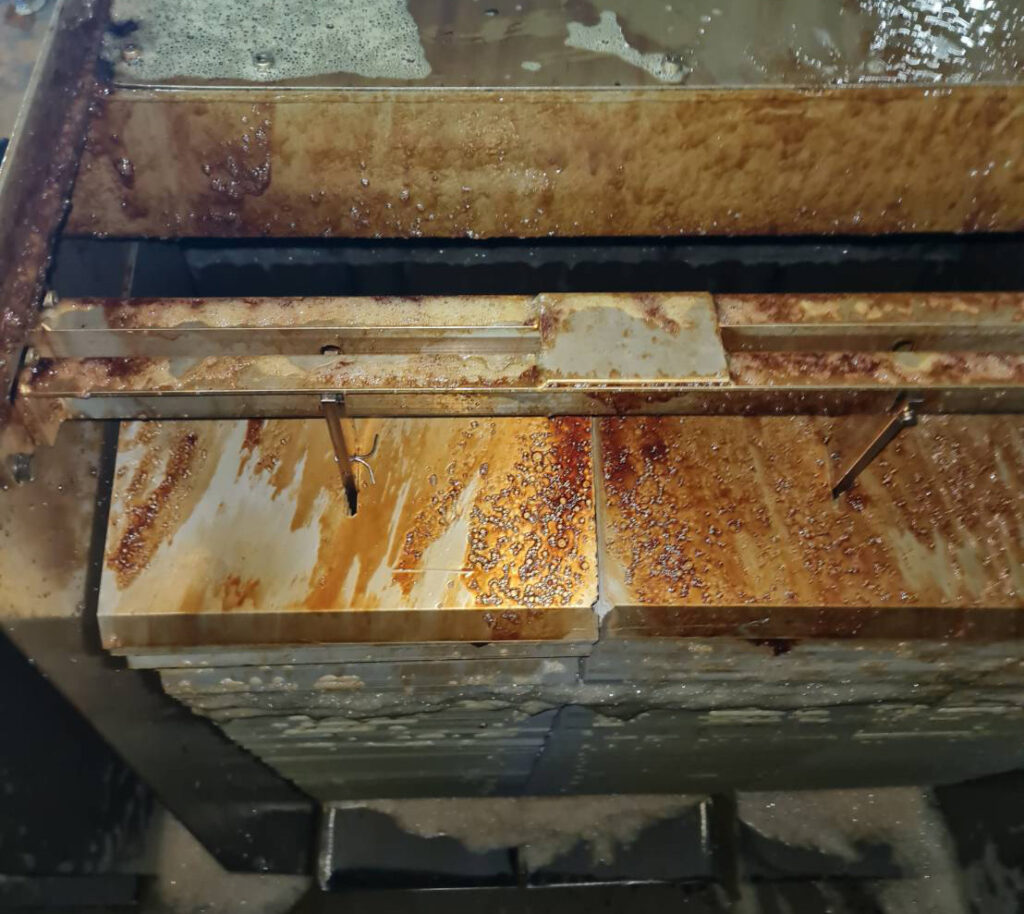


This oil oxidation occurs when water breakdown through Heat Exchanger or slow water leaking in the system and the water problem got noticed. New oil replaces the old oil from the reservoir. However, there is about 20% of the old oil left in the pipe line, cylinder, valve, pump that can not be drained out. So the new oil replacement is adding 80% of new oil and mixes with 20% of old oil. So the new oil mixture still have plenty of water in the new oil replacement in the oil reservoir.
New oil has plenty of Water Demulsifier Agent Additive that can is still able of depressing Water and hold them into Hydroxyl (OH–) that will transform into H2 Hydrogen and O2 Oxygen. The milky look of new oil replacement will slowly disappear from oil reservoir in the next 4-5 days after new oil replacement. This leads to believe that water in the oil is evaporated from the system. Water did not disappear but transform into H2 Hydrogen and O2 Oxygen.
H2 Hydrogen can easily react with Hydrocarbon Base Oil and its Additives to become Carboxylic Acid, thus increases Oil Acidity. All acid molecule always has Hydrogen inside. Oil Oxidation by products that came from Hydroxyl (OH–) will look like Gel as shown on the above photo.
After oil acidity increase, acidity will react with Elastomer of rubber O-RIng and Gasket causing Elastomer deterioration and getting hard and brittle. This will definitely affect the seal and gasket deterioration causing leaking oil from the reservoir within the next 6-9 months. User will notice more of leaked oil problems become omnipresence.
From hydroxyl (OH–) there will be plenty of O2 Oxygen in the oil. This excessive O2 Oxygen will react with Iron to become Iron Oxides and forms Rusting Internal Corrosion in the oil. Oxygen is also acting as Oxidation Catalyst when oil is heated.
Therefore, new oil replacement does not end as solution. It is only beginning of many equipment problems afterward if user doesn’t know how to provide proper Oil Contamination Control.
- Contact Information – OilPure Technologies, Inc.:
- P.O. Box 483976 • Kansas City • Missouri 64148 • USA • SKYPE ID: oilpure • LINE ID: oilpure
- Tel: 913-906-0400 • Mobile: 913-522-0272 • Fax: 913-906-9815
© Copyright, August , 2021
Document and information in this website is a proprietary information belonging to OilPure and is not allowed to reveal to public without OilPure consent.